Nmap (Network Mapper)
Description:
Nmap is an open-source network scanning tool widely used in the field of network security. It’s designed to discover devices and services on a network, providing detailed information about network infrastructure and security vulnerabilities.
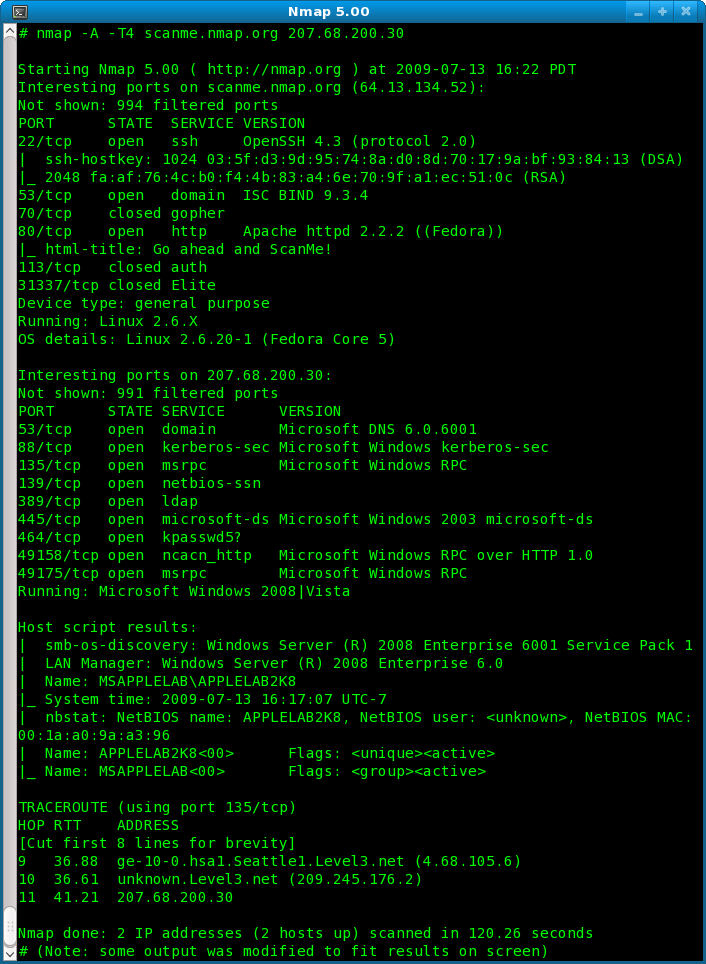
Image of NMap code
From nmap5-samplescan-706×964.png (706×964)
Basic Use:
- Network Inventory: Nmap is used to create an inventory of all devices connected to a network, including servers, workstations, network printers, routers, and switches.
- Security Auditing: It helps in identifying open ports, detecting the operating systems and software versions running on network devices, and consequently uncovering potential security vulnerabilities.
- Network Mapping: Nmap is employed to map out the layout of a network, showing how various devices are connected and communicating.
- Identifying Unauthorized Devices: It can detect unauthorized devices connected to a network, enhancing network security.
- Service Upgrade Schedules: By determining the software versions on network devices, it aids in planning service upgrades or patches.
Zenmap
Description:
Zenmap is the official graphical user interface (GUI) for the Nmap Security Scanner. It aims to make Nmap easier to use for beginners while providing advanced features for experienced Nmap users.
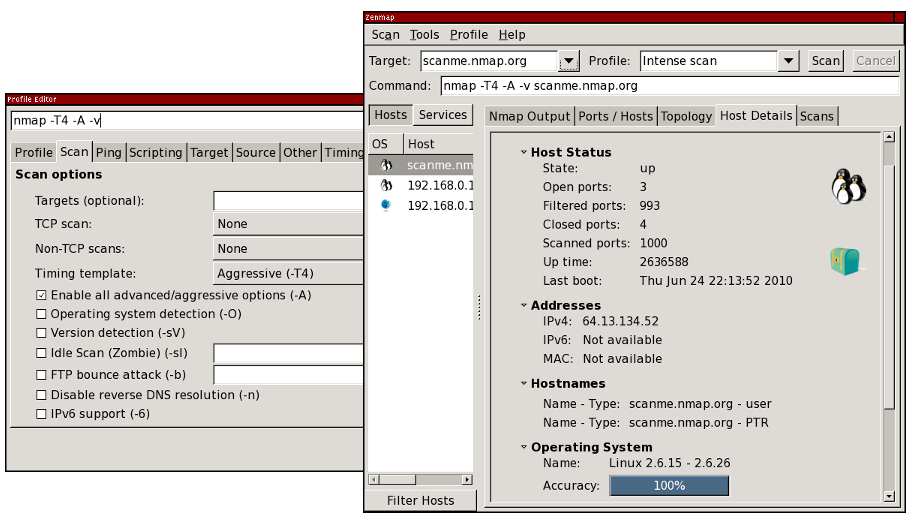
Image of ZenMap GUI from zenmap-multi-scaled-915×525.png (915×525)
Basic Use:
- Simplified Scanning: Zenmap simplifies the process of running Nmap scans by providing a user-friendly interface, making it more accessible to those who are less comfortable with command-line tools.
- Scan Analysis: It offers features for analyzing and visualizing the results of Nmap scans, such as network topologies and host details.
- Comparing Scan Results: Zenmap can compare the results of different scans to track changes in a network over time. This feature is particularly useful for monitoring network modifications and identifying new or altered devices and services.
- Saved Profiles and Scans: Users can save specific scan configurations as profiles for quick and consistent execution of routine scans.
- Target Testing: It can be used to test a specific device or range of devices on a network, allowing for focused security assessments.
Both Nmap and Zenmap are critical tools in the toolkit of network administrators, security professionals, and penetration testers. They offer powerful capabilities for network discovery, security auditing, and vulnerability detection.
Extra
NMAP
Nmap (Network Mapper) is a powerful and widely used open-source network scanning tool. It is designed to discover hosts and services on a computer network, providing information about open ports, running services, operating systems, and more. Nmap offers a range of features and options, including the ability to execute custom scripts called NSE (Nmap Scripting Engine) scripts. These scripts can be used to automate various tasks and perform specialized network scanning and enumeration.
Here are some common Nmap commands for port scanning along with their functions:
Basic TCP Port Scan:
Command: nmap <target>
Function: Performs a TCP port scan on the target host, scanning the most common ports (default: 1-1,000) to determine which ports are open.
Full TCP Port Scan:
Command: nmap -p- <target>
Function: Conducts a comprehensive TCP port scan on all 65,535 ports, providing a thorough analysis of open and closed ports on the target host.
TCP SYN/ACK Scan (Stealth Scan):
Command: nmap -sS <target>
Function: Utilizes TCP SYN/ACK packets to determine open ports. It’s a stealthy scan method, as it doesn’t complete the full handshake process.
UDP Port Scan:
Command: nmap -sU <target>
Function: Performs a UDP port scan to identify open UDP ports on the target host. UDP scanning is used for services that run over UDP instead of TCP.
Service Version Detection:
Command: nmap -sV <target>
Function: Detects the versions of services running on open ports. Nmap sends probes to the open ports to identify the application and its version.
OS Detection:
Command: nmap -O <target>
Function: Attempts to determine the operating system of the target host by analyzing various network fingerprints and response patterns.
Port Scan with Timing Options:
Command: nmap -T<0-5> <target>
Function: Adjusts the timing and aggressiveness of the scan. The higher the number (0-5), the faster and more aggressive the scan becomes.
Scan Multiple Hosts:
Command: nmap <target1> <target2> <target3> ...
Function: Allows scanning of multiple hosts simultaneously, providing information about open ports on each target.
Scan Specific Ports:
Command: nmap -p <port1,port2,port3,...> <target>
Function: Scans only the specified ports instead of scanning a range of ports. Multiple ports can be comma-separated.
Save Scan Results to a File:
Command: nmap -oN <filename> <target>
Function: Saves the scan results to a specified file in normal format, which can be reviewed later or used for further analysis.
These commands provide a starting point for conducting port scans using Nmap. Each command offers different functionalities and options, allowing you to customize your scanning approach based on your specific requirements and objectives
Here are a few examples of NSE scripts along with their functions and example results:
Script: http-title
Function: Retrieves the title of HTTP services running on open ports.
Result: Displays the title of the webpage hosted on the open HTTP service.
Script: ssl-heartbleed
Function: Checks if a target is vulnerable to the Heartbleed SSL vulnerability.
Result: Determines if the SSL service is susceptible to the Heartbleed vulnerability.
Script: smb-os-discovery
Function: Detects the operating system running on remote SMB (Server Message Block) servers.
Result: Provides information about the detected OS version and additional details.
Script: dns-zone-transfer
Function: Attempts a DNS zone transfer from a target DNS server.
Result: Retrieves a list of DNS records (e.g., domain names, IP addresses) associated with the DNS zone.
Script: ftp-anon
Function: Checks if an FTP server allows anonymous (unauthenticated) access.
Result: Determines if the FTP server permits users to log in anonymously.
Script: snmp-info
Function: Gathers system information from SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) enabled devices.
Result: Retrieves details such as device model, OS version, uptime, and network interfaces.
These are just a few examples of the many NSE scripts available in Nmap. The NSE scripts extend Nmap’s functionality, allowing you to perform specific tasks and gather detailed information about the target network or host.
It’s important to note that while Nmap is a legitimate and useful network exploration tool, it should be used responsibly and ethically. Unauthorized or malicious use of Nmap or its scripts can potentially violate network security and privacy. Always ensure you have proper authorization and adhere to applicable laws and regulations when conducting network scanning activities.

