Mesh
Mesh Topology Description
In a mesh topology, every node in the network is connected to every other node. This creates a network with multiple pathways for data to travel between any two nodes. The connections can be wired or wireless, and data can take any path to reach its destination, leading to a highly flexible and resilient network structure.
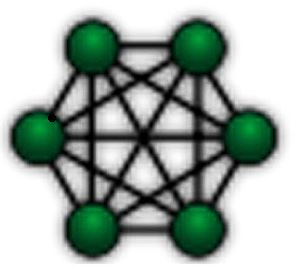
Image of a Mesh Topology
Why Mesh Topology is Used
Mesh topology is used primarily for its high redundancy and resilience. It’s ideal for networks where reliability is critical, such as in emergency services communication systems, military networks, or data centers. The multiple connections ensure that even if one part of the network fails, data can still be rerouted through other paths.
Benefits of Mesh Topology
- High Redundancy and Reliability: The multiple pathways ensure that the network remains operational even if one or several connections fail.
- Robust Fault Tolerance: The network can continue functioning seamlessly even in cases of hardware failure, as alternate paths can be used for data transmission.
- Enhanced Privacy and Security: Direct connections between nodes can enhance the privacy and security of communications.
- Optimal Load Balancing and Reduced Traffic: Multiple paths allow for balancing loads and reducing traffic bottlenecks.
- Easy to Scale: Additional devices can be added without significant changes to the network.
Drawbacks of Mesh Topology
- High Cost: The requirement for each node to connect to every other node results in high installation and maintenance costs, especially for large networks.
- Complex Configuration and Management: The large number of connections can make the network challenging to configure and manage.
- Increased Cabling: In a wired mesh network, the amount of cabling can be extensive, increasing costs and installation complexity.
- Potential for Redundant Connections: In smaller networks or less critical applications, the high level of redundancy might not justify the cost and complexity.
Comparison with Other Topologies
- Star Topology: Unlike star topology, mesh topology does not have a single point of failure, but it is more complex and expensive.
- Ring and Bus Topologies: Mesh topology provides higher redundancy and reliability compared to ring and bus topologies, which can fail if a single connection goes down.
- Tree Topology: Mesh topology offers more direct communication paths than tree topology, but with added complexity and cost.
- Partial Mesh Topology: A full mesh topology offers more redundancy than a partial mesh but at a higher cost and complexity.
Mesh topology is ideally suited for networks where reliability and data path diversity are of paramount importance and where the budget allows for the extra costs associated with its implementation and maintenance.
Extra
Let’s all join hands around the world!
